मेन्यू
बंद करना
अन्य नाम/उपप्रकार: आंख की नस (तंत्रिका) ट्यूमर, केयाज़्मेटिक ग्लिओमा, ऑप्टिक ग्लिओमा
ऑप्टिक पाथवे ट्यूमर एक प्रकार का ग्लिओमा है, यह ऐसा ट्यूमर है जो नस (तंत्रिका) कोशिकाओं को चारों और से ढकने और सहारा देने वाले ग्लायल सेल से विकसित होता है। बच्चों में होने वाले ऑप्टिक पाथवे ट्यूमर आमतौर पर कम श्रेणी के ट्यूमर होते हैं। ये दृष्टि प्रणाली की संरचनाओं के साथ विकसित होते हैं जिसमें आंख की नस (तंत्रिका), ऑप्टिक ट्रैक्ट और/या ऑप्टिक केयाज़्म शामिल हैं।
ट्यूमर के बढ़ने के साथ-साथ, दृष्टि प्रणाली की संरचनाओं पर पड़ने वाले दबाव से दृष्टि से संबंधित समस्याएं उत्पन्न हो सकती हैं। ऑप्टिक पाथवे ग्लिओमा पीयूष ग्रंथि और हाइपोथेलेमस के आसपास भी विकसित हो सकते हैं। स्थान के आधार पर, ट्यूमर एंडोक्राइन फ़ंक्शन और हार्मोन उत्पादन की प्रक्रिया को प्रभावित कर सकता है।
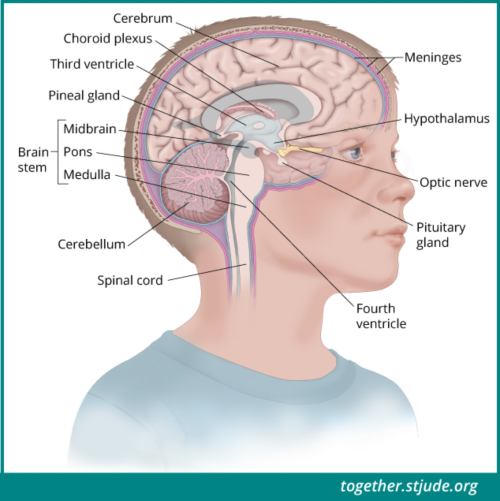
बच्चों में ऑप्टिक पाथवे ट्यूमर दृष्टि प्रणाली की संरचनाओं के साथ विकसित होते हैं जिसमें आंख की नस (तंत्रिका), ऑप्टिक ट्रैक्ट और/या ऑप्टिक केयाज़्म शामिल हैं।
ऑप्टिक पाथवे ट्यूमर का अनुपात बाल चिकित्सा में होने वाले सभी केंद्रीय तंत्रिका तंत्र (सीएनएस) ट्यूमर का 5% तक होता है। ये छोटे बच्चों और न्यूरोफाइब्रोमैटोसिस टाइप 1 (एनएफ1) वाले बच्चों में अधिक आम होता है।
ऑप्टिक पाथवे ट्यूमर का इलाज आयु, दृष्टि, एनएफ1 स्थिति, और ट्यूमर के स्थान जैसे कारकों पर निर्भर करता है। ऑप्टिक पाथवे ट्यूमर का इलाज करने के लिए सर्जरी, कीमोथेरेपी, और/या रेडिएशन थेरेपी का उपयोग किया जा सकता है। हालांकि, दृष्टि संबंधी प्रक्रिया और एंडोक्राइन फ़ंक्शन को पहुंचने वाली संभावित हानि के कारण इसका इलाज जटिल होता है। यह देखने के लिए कि बीमारी कैसे बढ़ती है, कुछ रोगियों को निगरानी में रखा जा सकता है।
ऑप्टिक पाथवे ट्यूमर के लक्षण निम्नलिखित सहित बहुत से कारकों पर निर्भर करते हैं:
Optic pathway tumor signs and symptoms may include:
स्थान के आधार पर, ऑप्टिक पाथवे ट्यूमर एंडोक्राइन फ़ंक्शन और हार्मोन उत्पादन की प्रक्रिया को प्रभावित कर सकते हैं।
चिकित्सक विभिन्न तरीकों से ऑप्टिक पाथवे ट्यूमर का आकलन करते हैं।
ऑप्टिक पाथवे ट्यूमर को, माइक्रोस्कोप के नीचे वे कैसे दिखते हैं इस आधार पर वर्गीकृत किया जाता है। ट्यूमर कोशिकाएं जितनी अधिकअसामान्य दिखती हैं, ट्यूमर उतनी ही उच्च श्रेणी का होता है। बच्चों में होने वाले अधिकांश ऑप्टिक पाथवे ट्यूमर कम श्रेणी के होते हैं। इसकी कोशिकाएं सामान्य कोशिकाओं से अधिक भिन्न नहीं दिखती हैं और ये धीमी गति से बढ़ती हैं। सीएनएस के अन्य भागों में इनके फैलने की संभावना कम होती है।
Rarely, pediatric optic pathway tumors may be high grade. These tumors are more aggressive, grow quickly, and can spread throughout the brain and spinal cord.
बच्चों में होने वाले ऑप्टिक पाथवे ट्यूमर के संबंध में लंबे समय तक जीवित रहने की दर उच्च (>90%) है। एनएफ1 वाले बच्चों में धीमी गति से बढ़ने वाले ट्यूमर हो सकते हैं जिन्हें निगरानी में रखते हुए देखा जा सकता है। जीवित रहने की उच्च दर होने के बावजूद, इन ट्यूमर का इलाज और प्रबंधन जटिल है। ऑप्टिक पाथवे ग्लिओमा से बचने वाले लोगों में दृष्टि से संबंधित समस्याएं होना आम होता है। ट्यूमर के स्थान के आधार पर, एंडोक्राइन फ़ंक्शन भी प्रभावित हो सकता है। इलाज और जीवन शैली में संतुलन बनाए रखने के लिए इलाजों की योजना बनाने हेतु एक बहुविषयक देखभाल टीम की आवश्यकता होती है।
Factors that influence prognosis include:
An early diagnosis helps preserve vision and eye health. The sooner that pressure on the visual system structures can be relieved, the more likely it is that vision will improve.
ऑप्टिक पाथवे ट्यूमर के लिए कोई एकल इलाज योजना नहीं है। क्योंकि आमतौर पर ये कम श्रेणी के ट्यूमर होते हैं, इसलिए इसमें पर्याप्त दृष्टि को बचाए रखना प्रमुख चिंता का विषय होता है। आंख की नस (तंत्रिका) ग्लिओमा का इलाज करने के लिए उपयोग किए जाने वाले इलाज बच्चे की आयु, दृष्टि हानि की सीमा, ट्यूमर के स्थान और आकार तथा इस बात पर निर्भर करते हैं कि बच्चे को एनएफ1 है या नहीं।
Treatment options include:
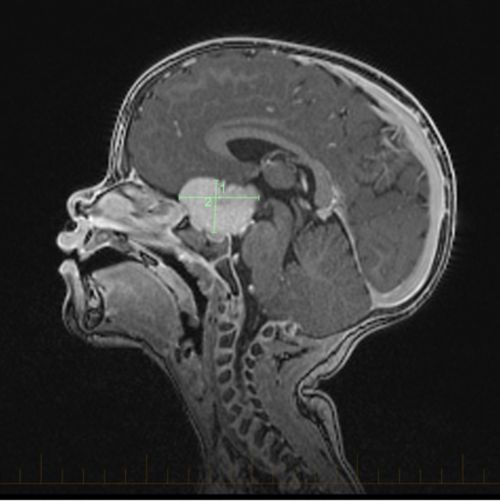
Doctors monitor patients using eye exams and periodic MRI scans. Indications of disease progression include worsening vision, increase in tumor size, or spread of disease.
चिकित्सक नेत्र परीक्षण और समय-समय पर एमआरआई स्कैन का उपयोग करते हुए रोगियों को मॉनिटर करते हैं। रोग बढ़ने के संकेतों में दृष्टि का खराब होना, ट्यूमर का आकार बढ़ना या कैंसर का फैलना शामिल है।रोगियों को लंबी अवधि तक मॉनिटर करने के लिए समय-समय पर इमेजिंग जांचें और व्यापक नेत्र परीक्षण का उपयोग किया जाता है। बहुविषयक देखभाल में पुनर्सुधार, स्नायुविज्ञान और एंडोक्रिनोलॉजी सहित विभिन्न प्रकार के विशेष क्षेत्र शामिल हो सकते हैं। ऑप्टिक पाथवे ट्यूमर से बचने वाले सभी लोगों में नेत्र संबंधी स्वास्थ्य खासतौर से महत्वपूर्ण होता है। नेत्र विशेषज्ञ द्वारा नियमित स्वास्थ्य देखभाल के भाग के रूप में वर्ष में कम से कम एक बार नेत्र परीक्षण करवाने की सलाह दी जाती है। बहुत से बच्चों में आजीवन काल तक दृष्टिहीनता रहती है और उन्हें दृष्टि संबंधी सहायता की आवश्यकता पड़ सकती है। अल्प दृष्टि से संबंधित विशेषज्ञ और स्कूल आवास, बच्चों को दृष्टि हानि के अनुकूल ढ़लने में मदद कर सकते हैं। आंखों को क्षति पहुंचने से बचाने के लिए सुरक्षात्मक चश्मा भी पहना जाना चाहिए।
—
समीक्षा की गई: जून, 2018