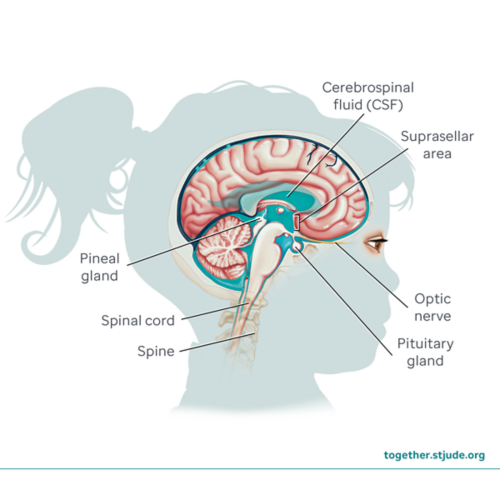
What are germ cell brain tumors?
Germ cell tumors (GCTs) of the brain and spinal cord are rare, but they are most often diagnosed in children and young adults.
These tumors usually develop in the pineal region of the brain (near the pineal gland) or suprasellar region of the brain (near the pituitary gland). They can also develop in the spinal cord.
Germ cell brain tumors can sometimes spread to other sites in the brain, spine, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). But they do not usually spread throughout the body.
Most germ cell brain tumors are treated with chemotherapy along with radiation therapy. Surgery may be used in some cases.
Symptoms of germ cell brain tumors
Signs and symptoms of a germ cell tumor depend on the tumor size and location.
As the tumor grows, it may cause cerebrospinal fluid to build up in the brain. This is hydrocephalus. It causes increased pressure in the brain. Pressure on the brain tissue can cause many symptoms of germ cell brain tumors.
Depending on the region affected, symptoms may vary.
GCT tumor symptoms (pineal region):
- Headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Changes in energy level (fatigue)
- Irritability
- Memory problems
- Vision changes:
- Double vision
- Trouble looking up
- Problems focusing on close objects
- Abnormal, repetitive eye movements without control (nystagmus)
GCT tumor symptoms (supracellar region):
- Changes in endocrine function may cause:
- Slowed growth
- Early or delayed puberty
- Increased thirst and urination (diabetes insipidus)
- Vision problems if the tumor is close to the optic nerve
- Memory problems
Risk factors for germ cell brain tumors
The cause for most germ cell tumors of the brain and spinal cord is unknown.
About 90% (9 out of 10) of these tumors occur in patients younger than age 20. Most cases develop in the early teen years.
Germ cell tumors are 2 to 3 times more common in males than females.
Diagnosis of germ cell brain tumors
Tests to diagnose germ cell tumors of the brain and spinal cord include:
- A physical exam and health history to learn about symptoms, general health, past illness, and risk factors.
- A neurological exam to assess brain function. This includes memory, vision, hearing, muscle strength, balance, coordination, and reflexes.
- Imaging tests to help identify the tumor, its size, and location.
- Blood and urine tests
- Complete blood count
- Blood chemistry studies that measure levels of blood sugar and other substances
- Tests to measure hormones made by the pituitary gland
- Tests for tumor markers, which are substances produced by cancer cells or other cells when cancer is present
- Biopsy to remove a sample of the tumor. A pathologist looks at the tissue under a microscope to identify the type of tumor.
- Lumbar puncture to look for cancer cells in the cerebrospinal fluid and to test for tumor markers
- Genetic testing of the tumor to find specific changes (mutations) to identify the type of tumor
Types of germ cell brain tumors
Types of germ cell brain tumors include:
- Germinoma (the most common type of GCT)
- Non-germinomatous germ cell tumor (NGGCT)
- Choriocarcinoma
- Embryonal carcinoma
- Immature teratoma
- Mature teratoma
- Mixed germ cell tumor
- Teratoma with somatic-type malignancy
- Yolk sac tumor/endodermal sinus tumor
In the pineal region, GCTs occur mostly in males, and the tumors are usually germinomas.
In the suprasellar region, males and females both get GCTs equally. Germinomas and NGGCTs develop with equal frequency.
Staging of germ cell brain tumors
These tumors rarely spread beyond the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). A germ cell tumor of the brain can spread to other parts of the central nervous system, including the spine and cerebrospinal fluid.
Germ cell tumors in the brain or spinal cord are described as newly diagnosed or recurrent.
Treatment of germ cell brain tumors
Treatment for germ cell tumors of the brain and spinal cord depends on several factors. These include:
- The tumor’s size and location
- The tumor type
- If the cancer has spread
- The child’s age and health
The main treatments for germ cell tumors of the brain and spinal cord are radiation therapy and chemotherapy. Clinical trials may be available as an option for some patients.
Radiation therapy for germ cell brain tumors
Radiation therapy is a key part of treatment for GCT. Radiation therapy is usually avoided in young children under the age of 3. This is because of possible damage to the brain while it is still developing.
Chemotherapy for germ cell brain tumors
Chemotherapy is often used along with radiation therapy. Chemo medicines may include carboplatin, etoposide, and ifosfamide.
For recurrent disease, patients may get high-dose chemotherapy with stem cell rescue.
Surgery for germ cell brain tumors
Surgery may be used to treat certain types of tumors. It is not often used to treat germinomas. However, because non-germinomas are often harder to treat, surgery may be used to remove as much of the tumor as possible. Surgery is usually used along with chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
In some cases, a shunt is placed in the brain to keep fluid from building up (hydrocephalus). This fluid causes increased intracranial pressure. It may cause many of the symptoms associated with germ cell brain tumors. A shunt is a small tube that drains cerebrospinal fluid to remove it from the brain and reduce pressure. The shunt may be temporary or permanent.
Prognosis for germ cell brain tumors
Your care team is the best source of information about your child's prognosis. The prognosis depends on several factors. These include:
- Your child’s age
- Type of germ cell tumor
- Type and level of tumor markers
- Tumor’s location
- Whether the tumor has spread
- Whether the tumor has recurred
Germinomas in children usually respond well to treatment. The survival rate is about 90% in the United States.
Certain types of germ cell tumors of the brain and spinal cord have a better prognosis than others. Many factors affect treatment and prognosis. Here is a general guide based on the tumor type:
Support for patients with germ cell brain tumors
Recovery and long-term effects of germ cell brain tumors in children and teens depend on the type of tumor and treatments received. Ongoing follow-up care, lab tests, and routine MRI scans can monitor patients after treatment.
Monitoring should focus on early detection of recurrence (cancer coming back) as well as long-term and late effects of treatment. Your child’s care team can help you decide the best plan for your child.
The impact of a brain tumor on a child’s quality of life varies widely. Some children with brain tumors show few lasting effects after treatment. Other children may have long-term problems.
Some problems are the result of injury to the brain from the tumor or surgery. Other changes may be due to long-term or late effects of chemotherapy or radiation.
Patients treated for brain tumors should be watched for problems such as:
- Weakness or problems with balance or coordination
- Problems in thinking, learning, memory, attention, or processing information
- Changes in behavior, emotions, or social function
- Speech, hearing, and vision problems
- Seizures
Patients with germ cell tumors of the brain and spinal cord are at risk for long-term problems in endocrine function. This could include diabetes insipidus and problems with pituitary gland function. Low pituitary function can lead to problems such as:
- Delayed growth
- Delayed puberty
- Fatigue
- Lower thyroid function
- Fertility or reproductive system problems
Some patients may need medicines that include hormone replacement.
School support is often needed after brain tumor treatment. Your care team can help you plan for neuropsychological testing and academic or work accommodations that may help your child. Psychological services can help with emotional, social, developmental, and cognitive needs.
Your child’s care team can help create a plan for ongoing care. It is important for patients to:
- Have regular checkups and screenings by a primary care provider.
- Share their survivorship care plan with all health care providers. This includes information about recommended health screenings, disease risk factors, and wellness habits.
- Maintain healthy habits, including physical activity and healthy eating
Questions to ask your care team