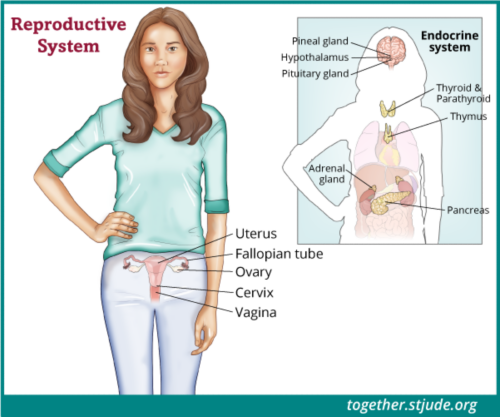
Egg (oocyte) freezing (cryopreservation)
Egg freezing is also called egg or oocyte cryopreservation. In this procedure, doctors remove eggs from the ovary and then freeze them. The patient gets hormones to stimulate the ovaries to produce eggs. The eggs are removed. Later the eggs can be thawed and fertilized with sperm in the lab to form embryos. They are then placed in a woman’s uterus to grow.
You can have eggs frozen if:
- You have had at least 1 period.
- You have at least 14 days before your cancer treatment starts or your cancer treatment ended 6 months or more ago.
- Your care provider believes you have enough healthy eggs for the procedure.
Egg freezing is only an option for girls who have started having menstrual cycles. This option is not always possible because cancer treatment must be delayed for a few weeks to harvest the eggs. It can also be a risk for patients with tumors that are sensitive to hormones.
Embryo freezing (cryopreservation)
Embryo freezing, also called cryopreservation, is another way of preserving fertility. But only women who have gone through puberty can have this option. Also, it requires a sperm donor.
The woman undergoes a procedure called in vitro fertilization (IVF). The woman gets hormones to stimulate the ovaries to produce eggs. The eggs are then removed. Embryos are created by joining together the sperm and eggs. They are frozen. Later in life, one or two embryos can be placed in the woman’s uterus with or without the help of medications.
Like egg freezing, this option requires a treatment delay and involves the use of hormones.
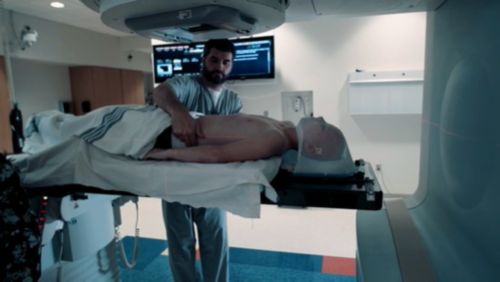
Ovarian transposition (oophoropexy)
This option is usually only offered if the patient is having another surgical procedure. This is because the procedure is invasive. During this procedure, surgeons move the ovaries away from the area receiving radiation therapy. The goal is to move the ovaries within the pelvis where they can still function but won’t be exposed to radiation.