Famille de sites Web de St. Jude
Découvrez nos recherches de pointe, nos soins aux patients de classe mondiale, nos opportunités de carrière et bien plus encore.
Accueil St. Jude Children's Research Hospital
- Informations pour les patients
- Éducation et sensibilisation

- Collecte de fonds
-
Cancers de l’enfant
Découvrez des informations complètes sur le cancer de l'enfant et de l'adolescent.
-
Troubles sanguins
Trouvez des informations sur les types de troubles sanguins chez les enfants et les adolescents.
-
Maladies infectieuses
Apprenez-en plus sur les maladies infectieuses chez les enfants et les adolescents.
Traitements, tests, et procédures
Apprenez-en plus sur les traitements, les tests, les procédures, les médicaments et les effets secondaires.
Apprenez-en plus sur la navigation et la gestion des soins médicaux pour les enfants et les adolescents.
- Équipe de soins pédiatriques
- Naviguer dans les soins de santé
- Soins cliniques et à domicile
- Nutrition clinique
- Prévention et contrôle des infections
- Gérer les médicaments
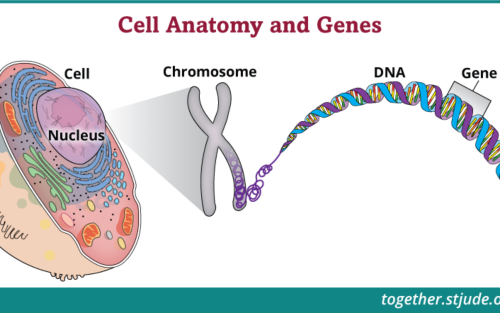
- Risque héréditaire et tests génétiques
- Psychologie et services de santé mentale
- Services de rééducation
- Soins palliatifs (soins de confort et de soutien)
- Fin de vie
Soutien émotionnel et vie quotidienne
Apprenez-en plus sur le soutien émotionnel et les ressources pour vous aider dans la vie de tous les jours.
Apprenez-en plus grâce à des vidéos, des blogs, des histoires et d’autres ressources.