Cardiac (Heart) Late Effects
What are cardiac late effects?
Some childhood cancer treatments may cause heart problems after treatment ends. These are called cardiac late effects. Cardiac means "related to the heart."
Radiation to the chest and a type of chemotherapy called anthracyclines are the main causes of cardiac late effects.
Most childhood cancer survivors do not have heart problems due to cancer treatment.
Healthy habits such as physical activity and a heart-healthy diet can help you manage or prevent many heart conditions.
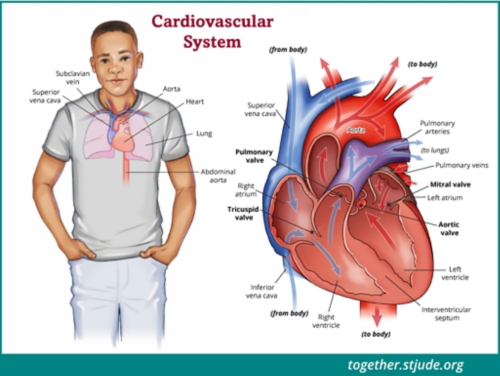
Learn how the heart works
- The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood to the body’s organs.
- It is at the center of the circulatory system, which is made up of a network of blood vessels, such as arteries, veins, and capillaries.
- An electrical system controls the heart and uses electrical signals to contract the heart's walls. When the walls contract, the heart pumps blood.
- Valves in the heart chambers keep the blood flowing in the correct direction.
- A healthy heart supplies the body with the right amount of blood at the rate needed to work well. If disease or injury weakens the heart, the organs won't get enough blood to work correctly.
Cardiac late effects that may occur
Cardiac conditions that may occur include:
- Coronary artery disease
- Abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmia)
- Scarred or leaky heart valves (valvular stenosis or insufficiency)
- Inflammation and scarring of the membrane surrounding the heart (pericarditis or pericardial fibrosis)
- Heart muscle weakening (cardiomyopathy)
Cardiomyopathy can get worse over time. It can lead to heart failure.
Causes of cardiac late effects
Anthracyclines
Anthracyclines are medicines used to treat many types of cancer.
These medicines include:
Anthracyclines can damage the heart muscle (cardiomyopathy). This damage can include heart failure. The risk of developing this condition increases with the amount of medicine given (dosage).
Anthracycline dosage (cumulative)
|
Risk of heart failure |
|---|
Less than 100 mg/m2
|
Low
|
More than 250 mg/m2
|
Moderate |
| 250 mg/m2 or greater |
High |
Chest radiation
Radiation given near the heart is a risk factor for heart disease. The risk increases with the amount of chest radiation given (dosage).
Radiation dosage
|
Risk
|
|---|
<15 Gy
|
Low |
15 Gy–<30 Gy
|
Moderate |
| 30 Gy or more |
High |
Anthracyclines and chest radiation
Survivors who had both anthracyclines and chest radiation have the highest risk.
Other risk factors for cardiac late effects
- Family history of heart disease
- Other health problems:
Diagnosis of cardiac late effects
At first, survivors may not have symptoms. But heart disease may be present.
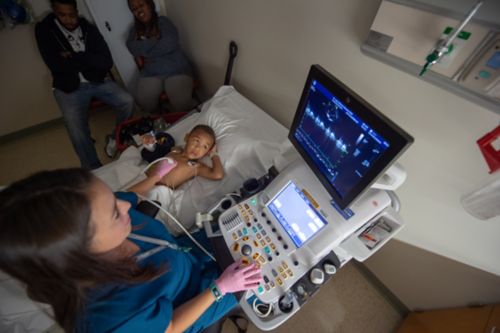
An echocardiogram (echo) is an easy, non-invasive way to detect heart disease before symptoms develop. It uses sound waves to make images of the heart.
Symptoms of heart disease
Patients may have:
- Coughing and wheezing that does not go away
- Heart racing or throbbing
- Irregular heartbeat
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Swollen feet and ankles
- Dizziness and feeling lightheaded
- Fainting
- Severe fatigue
- Sweating
- Nausea
What you can do about cardiac late effects
Cancer survivors can do things to promote heart health:
- Know your risk of developing heart problems. Ask your doctor if your treatments may increase your risk for heart disease.
- Share a copy of your survivorship care plan with your health care providers.
- Have regular check-ups.
- Have echocardiograms and other screenings as recommended in your survivorship care plan. Guidelines depend on the treatment you received.
- Talk to a cardiologist (heart doctor) if there are signs of damage to the heart.
- Get treatment for conditions that affect heart health.
- Have good health habits.
Heart-healthy habits
Habits that promote heart health include:
Questions to ask about cardiac late effects
- What is my risk of having heart problems?
- Does the treatment I received put me at higher risk for heart problems?
- Do I need an echocardiogram?
- Am I at risk of other complications from childhood cancer treatment?
- What can I do to lessen my risk of heart problems?
- What can I do to lower my anxiety about having heart problems?
Key points about cardiac late effects
- Some childhood cancer treatments may cause heart and blood vessel problems after treatment ends. These are called cardiac late effects.
- Chest radiation and chemotherapy with anthracyclines are the main causes of cardiac late effects.
- It is important to know your risk for developing heart problems, so that you get screening and/or recognize symptoms early.
- There are ways to manage many conditions.
- Heart-healthy habits (such as regular exercise, good nutrition, not smoking, keeping a healthy weight) can help prevent cardiac late effects.
—
The Together by St. Jude™️ online resource does not endorse any branded product mentioned in this article.
-
Physical Activity After Cancer
Most people know that physical activity is good for health. However, for cancer survivors, being active is even more important.
-
Survivorship Care Plans
A cancer survivorship care plan is a record of your cancer treatments and follow-up care plan. Learn more about cancer survivorship care plan.
-
Healthy Eating After Cancer
Healthy eating is important for everyone, but good nutrition is particularly important for childhood cancer survivors. Learn more about nutrition after cancer.