St. Jude Family of Websites
Explore our cutting edge research, world-class patient care, career opportunities and more.
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital Home

- Fundraising
-
Childhood Cancers
Explore comprehensive information about childhood and adolescent cancer.
-
Blood Disorders
Find information about types of blood disorders in children and adolescents.
-
Infectious Diseases
Learn more about infectious diseases in children and adolescents.
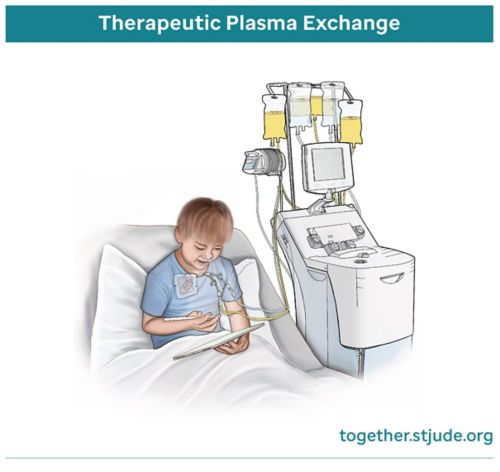
Treatments, Tests, and Procedures
Learn about treatments, tests, procedures, medicines, and side effects.
Learn about navigating and managing medical care for children and adolescents.
- Pediatric Care Team
- Navigating Health Care
- Paying for Medical Care
- Clinical and Home Care
- Clinical Nutrition
- Infection Prevention and Control
- Managing Medicines
- Inherited Risk and Genetic Testing
- Psychology and Mental Health Services
- Rehabilitation Services
- Palliative Care (Comfort and Supportive Care)
- End of Life
Emotional Support and Daily Life
Learn about emotional support and resources to help with day-to-day living.
Learn more through videos, blogs, stories, and other resources.