What is beta thalassemia trait?
Beta thalassemia trait is a change (mutation) in a gene that helps make hemoglobin in red blood cells. People with the trait have a missing or damaged gene. Beta thalassemia trait is also called beta thalassemia minor.
A trait is different from a disease
Most people with beta thalassemia trait have no signs or symptoms of illness. The trait can sometimes cause mild anemia. But it normally does not cause serious problems.
People with beta thalassemia trait do not have beta thalassemia disease or sickle cell disease. They cannot develop the conditions later in life. But they can pass the genes for beta thalassemia or sickle beta thalassemia on to their children.
- Beta thalassemia is an inherited blood disorder that causes you to make fewer red blood cells and less hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a protein that carries oxygen from the lungs to all parts of your body. There are two parts of hemoglobin: alpha globin and beta globin. The specific hemoglobin protein affected in beta thalassemia is the beta globin.
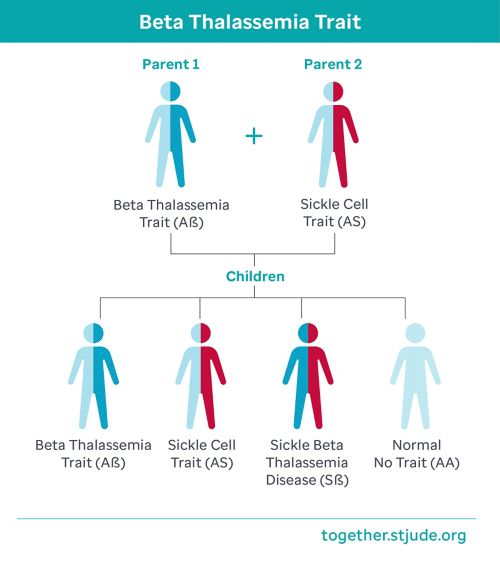
- Sickle beta thalassemia is a type of sickle cell disease. Depending on the amount of hemoglobin produced, a person may have sickle beta plus thalassemia or sickle beta zero thalassemia. A person with sickle cell disease has red blood cells that can sickle or become banana shaped. Sickle cell disease is a lifelong condition that can cause serious health problems. People with sickle cell disease need ongoing medical treatment. Learn more about sickle cell disease.
Risk factors for beta thalassemia trait
Beta thalassemia trait is common in people whose ancestors came from Africa, Asia, the Middle East, or the Mediterranean region. But it is possible for a person of any nationality or ancestry to have beta thalassemia trait.
Tests for beta thalassemia trait
A blood test can let you know if you have beta thalassemia trait. It may be done as part of newborn testing or genetic screening. Your doctor may also recommend testing if someone in your family has beta thalassemia.
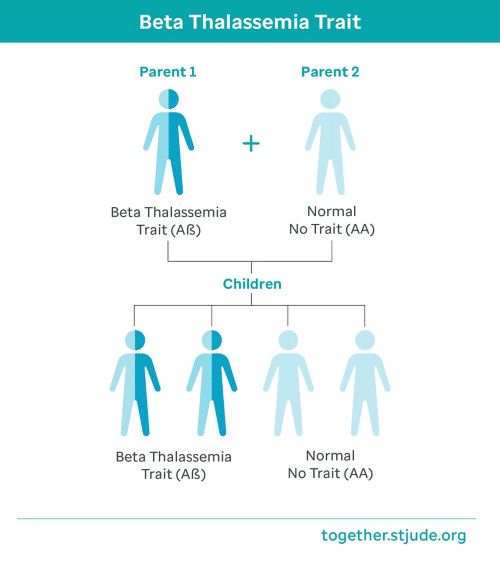
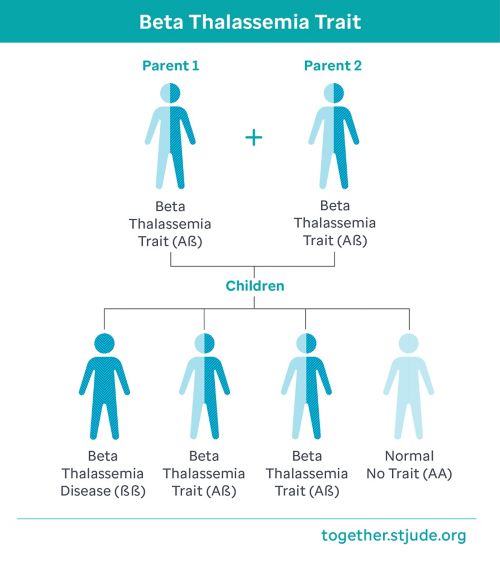
How beta thalassemia trait is inherited
Beta thalassemia runs in families. Like eye color or hair color, the genes for thalassemia trait are inherited, or passed from parents to children. Whether a child has the blood disorder depends on if they inherit the trait from one or both parents.
The severity of symptoms depends on the type of beta thalassemia a person has.
- Beta thalassemia trait (beta thalassemia minor) causes no symptoms or mild anemia symptoms.
- Beta thalassemia intermedia causes mild to moderate anemia.
- Beta thalassemia major (Cooley’s anemia) causes more severe anemia. This condition is known as “transfusion-dependent thalassemia” because it requires lifelong blood transfusions.
Beta thalassemia disease is a lifelong blood disorder that can cause serious health problems. People with this disease need medical treatment.
To learn more about trait conditions, talk to your doctor or genetic counselor. Your care team can give you more details about your trait status and that of your child.