What is vitamin D deficiency?
A vitamin D deficiency is a condition where a person has low levels of vitamin D in the body. Vitamin D is an important nutrient for health. It helps the body absorb calcium. Without enough vitamin D, bones can become soft and weak.
Symptoms of vitamin D deficiency
Low levels of vitamin D can cause:
- Bone pain
- Muscle weakness
- Joint problems
- Weak or thin bones (osteoporosis)
- Bone fractures
In children and teens, low vitamin D levels can cause bones to grow poorly, leading to shorter height than expected.
Causes of vitamin D deficiency
Factors that increase your child’s risk for having low vitamin D include:
- Medical conditions such as sickle cell disease
- Being overweight or obese
- Darker skin pigment
- Staying out of the sun or using sunscreen
- Kidney or liver disease
- Not being able to absorb vitamin D through the digestive system because of inflammatory diseases, surgery, or radiation therapy
- Certain medicines, such as steroids, laxatives, HIV treatments, and those used to treat seizures and fungal infections
Vitamin D Deficiency and Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease, can put your child at higher risk for low vitamin D levels. Treatment of vitamin D deficiency in patients with sickle cell disease may help reduce pain and protect bone health.
Diagnosis of vitamin D deficiency
Your child’s care team will do a blood test to test vitamin D levels.
Treatment of vitamin D deficiency
If your child has low levels of vitamin D, your health care provider may prescribe a vitamin D supplement. Be sure your child takes the medicine exactly as prescribed.
Too much vitamin D can be harmful. Always check with your health care provider before taking any over-the-counter vitamins or supplements.
How to prevent vitamin D deficiency
Get enough vitamin D through the diet
Be sure your child eats a healthy diet including foods higher in vitamin D. Vitamin D is found in certain foods such as:
- Milk
- Fatty fish such as tuna and salmon
- Fortified Orange juice
- Fortified Cereal
- Yogurt
- Egg yolks
- Mushrooms
- Cheese products
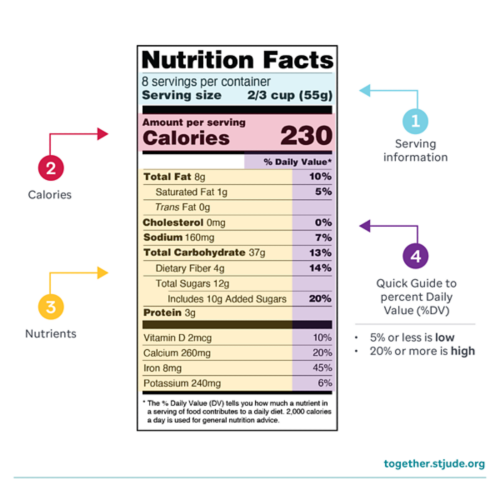
Check food labels. Look for labels that say, “vitamin D fortified.” On the nutrition facts label, check the amount of vitamin D. Babies need 400 IU of vitamin D each day. Children and teens need 600 IU of vitamin D each day. Learn how to read food labels.
Get sunlight during the day
Vitamin D is also made by the body through sun exposure. But too much sun exposure can increase your child’s risk for skin cancer. It is important to protect skin from the sun by using sunscreen and to limit time spent outdoors.
Vitamin D is important for your child’s health. Talk to your care team to understand your child’s risk for vitamin D deficiency.
—
Reviewed: September 2024