Menu
Close
Back
Welcome to
Together is a new resource for anyone affected by pediatric cancer - patients and their parents, family members, and friends.
Learn MorePatient Education at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital offers information and support to help patients and family caregivers navigate the care journey. Find patient education on a broad range of topics.

Learn about clinical care, treatment, and supportive therapies.

Learn about cancer types, blood disorders, and other health conditions.

Learn about blood disorders, complications, medical care, treatment side effects, daily living, and more.
Learn about types of medical equipment and their use.

Learn about types of medicine and how to use them safely.

Learn ways to manage practical needs and support physical, social, and mental health of patients and families.

Learn about short-term and long-term effects of diseases and treatments and find ways to manage them.
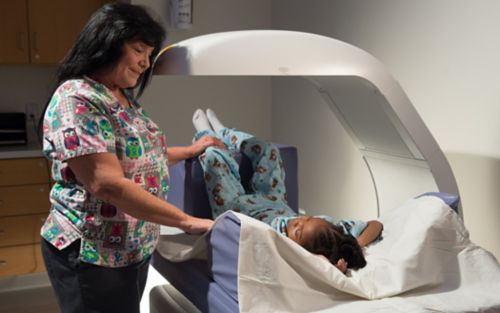
Learn what to expect before, during, and after lab tests, imaging, and other medical procedures.
To learn more about Patient Education at St. Jude, please contact patienteducation@stjude.org.
For questions about St. Jude, your child’s care, or instructions you were given, please contact your clinic or call 1-866-2STJUDE. If your child is a St. Jude patient and you have an urgent question or concern, ask to speak to the Nursing Coordinator on duty.
This information is general education and does not replace medical advice. Questions about individual health concerns or specific treatment options should be discussed with your health care provider. If you print or download this content, it is considered accurate for 72 hours, after which it is expired. Please return to Together to ensure you have the latest, up-to-date information.